A Conversation with Don Teng
The Logistics & Supply Chain Management Society
OCTOBER 17, 2022
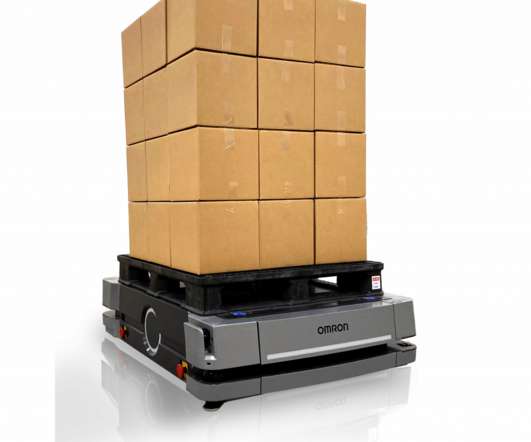
With the use of more data analytics and AI inside the warehouse, we can also expect a very healthy growth in deployment of robotics & AI solutions– ranging from WMS integration (perhaps through cloud) to multiple modes of material transfer (both horizontal and vertical), automated cross-docks, picking, sorting, packaging, etc.













Let's personalize your content