Traceability is a digital solution that enables companies to effectively track their products from origin to consumer by utilizing digital markers for identification. Various traceability solutions exist, including Digital Traceability, Laboratory Traceability, and Mapping Traceability.
With the growth of the market for high-quality food products, the importance of traceability and origin verification has increased significantly. These measures are crucial in protecting brands and ensuring ongoing consumer satisfaction.
58% of consumers are willing to pay a premium if it supports local farmers.
In food production, consumers have a strong desire to have complete visibility into their food's origin and production methods. Research conducted by Label Insight revealed that 81% of consumers actively seek more information about where their food is grown or raised before purchasing. Moreover, 58% are willing to pay a premium if it supports local farmers, while 57% will only buy items certified as organic or non-GMO (genetically modified organisms). This highlights the growing importance of traceability in meeting consumer demands and building trust in the food industry.
The expansion of global supply chains has introduced complexities and increased the length of the journey that products take from farm to table. Unfortunately, this also raises the opportunity for fraudulent activities to occur. Dishonest individuals may use deceptive practices such as mislabeling, substituting premium ingredients with lower-cost substitutes, or making false claims about a product's origin or qualities. These actions allow them to sell lower-quality products at higher prices, resulting in consumer deception and substantial profits.
The expansion of global supply chains has introduced complexities and increased the opportunity for fraudulent activities.
Food fraud is a global issue affecting all industries, posing risks to food safety and biosecurity. Biosecurity measures are essential to prevent the introduction and spread of disease-causing organisms in agriculture and related environments. Biosecurity incidents occur when products are contaminated with pathogens, chemicals, or other harmful substances that can compromise health and safety.
This fraudulent behavior can lead to unnecessary costs and significant damage to a company's reputation if consumers believe they have been misled into purchasing something other than what was advertised. Preventing such occurrences through robust traceability measures becomes crucial in maintaining consumer trust and safeguarding against financial and reputational consequences.
Traceability solutions offer diverse operational approaches, including:
- Digital Traceability: Digital traceability involves tracking a product throughout its entire lifecycle. This is achieved by utilizing barcodes and RFID tags that can be scanned at every process step. The collected data from these scans is stored in an online database. Companies can gain comprehensive visibility into their supply chains by employing this method. It ensures adherence to quality control procedures and enables real-time monitoring of inventory levels.
- Laboratory Traceability: Laboratory traceability leverages testing to provide valuable information about a product's origin, authenticity, and purity before it reaches consumers. Samples taken from crops during harvest are analyzed, revealing precise details about the chemicals used during production and the required amount of fertilizer based on soil composition analysis. Laboratory testing also determines product quality and ensures its safety for consumption. It offers vital insights into crop cultivation practices, enabling farmers to make informed decisions about land management techniques.
- Mapping Traceability: Mapping traceability involves identifying, recording, and visually representing the flow of products throughout the supply chain. It entails creating a detailed product journey record, including origins, destinations, and intermediate steps. Critical information such as ingredient sources, processing and packaging facilities, transportation routes, and points of sale are documented. This mapping process enables stakeholders like regulators, manufacturers, and consumers to track and verify food products' authenticity, safety, and quality. It aids in identifying potential risks, enhances transparency, and ensures accountability within the food supply chain.
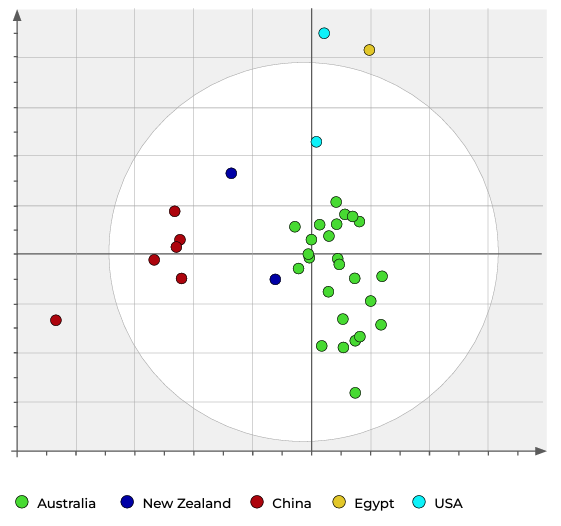
Australia has successfully conducted a laboratory traceability project to establish the National Isotope and Trace Element (NITE) Profile for Australian citrus through scientific testing. This groundbreaking study is the first of its kind and has achieved the identification of Australian oranges at both regional and international levels.
This accomplishment is a significant milestone in ensuring that consumers receive authentic Australian fruit products and safeguarding the country's reputation as a leading producer of premium citrus.
Differences in isotope ratios and trace element contents effectively trace food products due to the unique profiles.
Isotope and trace element analysis for origin verification has been employed in various food commodities, including wine, avocado, fruit juices, rice, and animal-derived products. Differences in isotope ratios and trace element contents provide an effective means of tracing food products due to the unique profiles influenced by geology, environmental conditions, and agricultural practices. In agricultural products like fruit, isotope ratios vary based on local geology, climate, environmental conditions, and farming techniques. As a result, they offer an atomic-level identification specific to a particular product and region, which cannot be tampered with or altered.
The methods and results obtained so far are promising. However, it is essential to acknowledge that the testing and development of results still require significant time, expertise, and expense.
As with any technology, further development will lead to the availability of rapid screening methods that are more affordable and faster, potentially even in real-time. Such advancements will impact the food industry and have implications for products across various industries. Imagine being able to trace the origin of gold from specific mines, track consumer electronics back to their designated factories, ensure drug traceability with necessary approvals, or monitor the shipment of oil or coal on bulk ships.
As with any technology, further development will lead to the availability of rapid screening methods.
To apply traceability in your industry and protect your products from fraud, consider answering the following strategic questions:
- What is the main problem you are trying to solve? - Identify the specific challenge or issue you aim to address through traceability measures.
- How can you apply traceability in your industry to prevent fraud, ensure security, support claims, and enhance brand and customer trust? - Explore how traceability solutions can be tailored to your industry to mitigate fraud, enhance security measures, validate product claims, and build customer trust.
- What are the benefits of implementing a traceability solution? - Consider the advantages a traceability solution can bring to your business, such as improved product integrity, supply chain transparency, enhanced customer confidence, and reduced risk of counterfeit products.
- What are the costs associated with implementing a traceability solution? - Assess the financial implications of adopting a traceability solution and weigh them against the potential benefits. Consider initial setup costs, ongoing maintenance expenses, and training requirements.
- How can you get started with a traceability solution? - Evaluate the steps required to implement a traceability solution within your organization. This may involve identifying suitable technology providers, establishing data collection and management processes, and ensuring proper integration with existing systems.
By addressing these strategic questions, you can pave the way for introducing a traceability solution that aligns with your industry's needs and helps protect your products from fraudulent activities.
To implement a traceability solution, it is vital to understand your industry's specific requirements and identify the most suitable technology and data management systems. Working collaboratively with key stakeholders, such as suppliers, distributors, and regulatory bodies, is critical for the initiative's success. Additionally, investing in employee training and education will be instrumental in ensuring a seamless implementation process.
In summary, by adopting a comprehensive and customized approach to traceability in your industry, you can effectively tackle significant challenges, safeguard against fraud, strengthen security measures, validate claims, and enhance your brand reputation and customer trust. By carefully evaluating the specific problem you aim to solve, weighing the potential benefits against associated costs, and meticulously planning the implementation process, you can leverage traceability to gain a competitive edge and establish a strong foundation for your business.

Comments