Increasing Sustainability for Automotive Manufacturers
Digital twins make industrial robotics more sustainable for automotive manufacturers. Learn the benefits of robotics virtual twin (RVT) tools.

Robotics Digital Twins in Automotive Manufacturing
Robotics virtual twin (RVT) technology is helping automotive manufacturers become more sustainable. With growing regulatory pressure on manufacturers, sustainability has become an urgent priority. While 34% percent of today’s biggest companies have committed to zero-emissions goals, 93% will miss their targets unless they double their emission reduction rates by 2030.
Seeking sustainable manufacturing solutions, auto industry executives have turned to robotics automation to increase efficiency. But while robots can build cars faster, they also can scale up inefficient processes, potentially multiplying waste and energy consumption. Robots themselves require resources that consume materials and energy.
To offer a way out of this dilemma, robotics virtual twins provide manufacturers with a connected digital development environment to reduce material waste and cut energy consumption. It can thereby increase the amount of sustainable car manufacturers. Here’s how RVT can help automotive manufacturers reduce environmental impact and meet sustainability goals.
Why Robotic Automation is Not Enough for Sustainability
On the surface, robotic automation may seem like a step toward more sustainable practices. Taking a deeper look at its pros and cons reveals a risk of doing more harm than good.
On the pro side, automation offers several advantages for supporting sustainability:
• Robots reduce material waste caused by human error, relying on precise programming instructions and accurate sensors. For example, automated laser cutting cuts sheet metal more accurately than human eyes and hands.
• Some factors contributing to energy consumption are reduced. A single robot produces parts more efficiently in less time than multiple human workers, consuming fewer resources per unit of output. Robots can work in environmental conditions that require less energy than human workers, such as low temperatures and dim lighting.
• Sorting robots can recycle materials more efficiently than humans. By using AI, sorting robots identify and separate items with speed and accuracy impossible with manual methods.
Environmental Implications of Robot Automation
Despite these overt benefits, a deeper look at the environmental implications of robotic automation reveals some hidden drawbacks that can offset sustainability gains. Some of these disadvantages include:
• Robotic equipment requires energy to operate, increasing the energy intensity of production processes. Industrial and manufacturing robots consume over 21,000 kilowatt-hours (kWh) a year.
• Increased use of electronic appliances and equipment produces more electronic waste.
• Robotic efficiency enables companies to scale up production, increasing energy usage during manufacturing and shipping processes.
These downsides to automation threaten to neutralize the sustainability benefits of robotics. According to a McKinsey industrial robotics survey, just 52% of automation deployments cause a positive impact on environmental sustainability. On the other hand, 45% had a neutral effect, and 3% were found to have a negative effect.
To realize the environmental benefits of robotics automation, manufacturers need to integrate robots into sustainability planning in a way that overcomes these drawbacks and promotes net improvements. This includes making robots themselves more environmentally friendly, and that is where robotics virtual twin technology can help.
Robotics Virtual Twin Technology and Manufacturing Sustainability
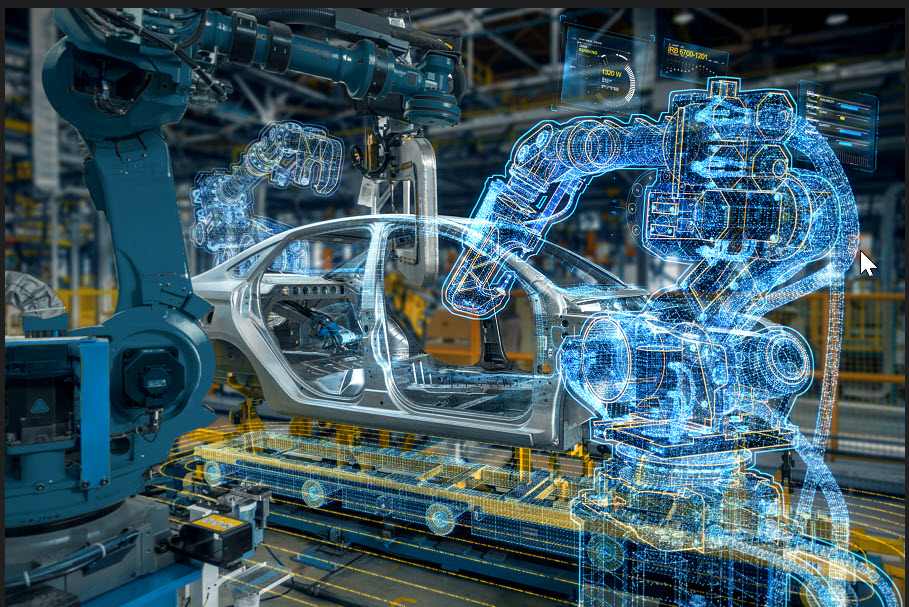
A robotics virtual twin is a digital model connected to a physical product or process that it represents. For instance, an RVT might represent a robot arm that welds body panels, or it might simulate the entire process of a robot assembly line producing car bodies.
Manufacturers typically adopt virtual twins to optimize efficiency. By coupling a robot or robotic process with a virtual twin, manufacturers can digitally track performance, simulate adjustments, test scenarios and optimize productivity. Live feedback from the twin’s digital counterpart enables companies to test and develop innovations faster than ever before, maximizing the full potential of robotics solutions.
Many auto manufacturers use robotics virtual twins and fewer may realize that RVT technology offers a way to improve the sustainability of automated processes. Virtual twins not only improve production efficiency, but they also can enhance energy efficiency.
Just as robotics virtual twins can model production processes, they can simulate the environmental impact of automated procedures, including the impact of robots themselves. This enables RVTs to reduce material waste and cut energy consumption used in automated processes.
Robotics Digital Twins Reduce Material Waste
Virtual twins can optimize production processes to minimize factors that cause material waste. Common sources of waste include:
• Inefficient design choices that require unnecessary material or generate excessive scrap
• Errors, such as inaccurate measurements
• Unproductive workflows that require wasted movements and resources
Robotic virtual simulations can mitigate these factors by applying corrective strategies to both products and robots that create products. RVT simulation can:
• Test designs before physical implementation to identify and reduce sources of waste
• Correct errors in a digital environment before physical waste is generated
• Optimize workflows to shorten steps and save resources
DELMIA, from Dassault Systèmes, delivers these benefits through a virtual twin experience that integrates RVT technology with the CATIA computer-assisted design collaboration platform. In CATIA, your team can create 3D models and animations of products and robots, experience how they look and behave in motion and optimize their parameters.
DELMIA helps you transform your CATIA 3D models into actionable virtual twins of your products and processes, including your robots. This seamlessly integrates your modeling and simulation with real-time feedback from your physical equipment. In so doing, you gain the ability to model and minimize material waste. You can identify exactly where waste is being generated, test reduction tactics and optimize your waste reduction strategies.
Robotics Virtual Twins Cut Energy Consumption
Virtual twin technology also helps reduce factors that impede energy efficiency. RVT lowers energy consumption by using two main strategies:
• Accurate system modeling lets manufacturers model and optimize the energy consumption of automation processes. RVT can calculate precise variables that influence energy consumption, such as mass, distance and time. This allows accurate estimates of critical energy measures such as potential energy, kinetic energy, rotational energy and friction. With this information, you can predict, manage and optimize energy usage.
• Real-world simulation of robot motion replicates the actions of robots themselves. For example, you can determine exactly how much energy a robot consumes when assembling a windshield and identify ways to reduce consumption.
DELMIA Robotics supports these strategies by letting you connect with your robot vendor’s software, providing simulations with virtually 100% accuracy. The Dynamic Attributes command lets you automatically calculate the physical variables of systems. The Digital Readout panel gives you real-time data on energy consumption generated by robots, down to individual robot joints. You gain a complete, holistic view of your energy consumption and how to manage variables that can reduce inefficiency.
Automotive Manufacturing with Robotics Virtual Twin
For auto manufacturers struggling to meet regulatory requirements, robotics virtual twins offer one of today’s most accurate, powerful tools for decreasing environmental impact. The ability to accurately simulate and test products and processes in a digital environment empowers you to reduce physical waste and energy consumption.
See more on sustainable manufacturing
Want to learn more about how to increase sustainability in your automotive manufacturing processes? Download our eBook, “Future-Proof Transportation & Mobility with Sustainable Manufacturing” today to explore how DELMIA Robotics can help.

