In today’s fast-paced business landscape, having an efficient supply chain department structure is more important than ever. A streamlined supply chain can make a significant impact on the overall success of a business, improving operational efficiency, increasing customer satisfaction, and driving revenue growth. But how exactly can businesses achieve this level of efficiency? This article describes a streamlined supply chain department, ultimately leading to increased productivity and profitability.
In essence, a structured supply chain department as described in the blog can help you deliver the right supply chain strategy and goals which helps cost reduction, improve customer service, on-time delivery, and better working capital. By optimizing the supply chain, businesses can minimize costs, reduce lead times, and improve customer service.
The Purpose of the Supply Chain Department Structure
The supply chain department plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth flow of goods and services from the point of origin to the point of consumption. While Its primary purpose is to manage the entire process, from procurement to delivery, efficiently and cost-effectively, it also coordinates with production to automate processes and planning, etc.
To achieve this, the supply chain department needs strong coordination and collaboration with other departments, such as marketing, finance, and Sales. By aligning the goals and objectives of each department, businesses can create a seamless supply chain that maximizes efficiency and minimizes waste.
Watch What is Marketing Procurement? on our SCMDOJO YouTube Channel!
Why do you need a structured Supply Chain Department?
Even complex businesses can benefit from a well-organized supply chain department. Here’s why a structured approach is important:
Efficiency
A structured department creates a clear division of labor and defines processes for procurement, production, distribution, and returns. This avoids duplication of efforts and ensures a smooth flow of goods and services.
Cost Reduction
By streamlining operations, a structured department can minimize waste and unnecessary spending. This might involve optimizing inventory levels, negotiating better deals with suppliers, or implementing just-in-time manufacturing techniques.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
A structured department is better equipped to handle customer demands. By ensuring on-time deliveries and minimizing stockouts, they can directly improve customer satisfaction.
Risk Management
The department can proactively identify and address potential risks in the supply chain, such as material shortages, natural disasters, or political instability. Furthermore, a structured approach allows for contingency plans and smoother handling of disruptions.
Data-Driven Decisions
The structure provides a framework for collecting and analyzing data across the supply chain. This data can be used to identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions about sourcing, production, and distribution.
In short, a structured supply chain department acts as the backbone of a company’s ability to get the right products to the right customers at the right time, all while keeping costs under control and minimizing risks.
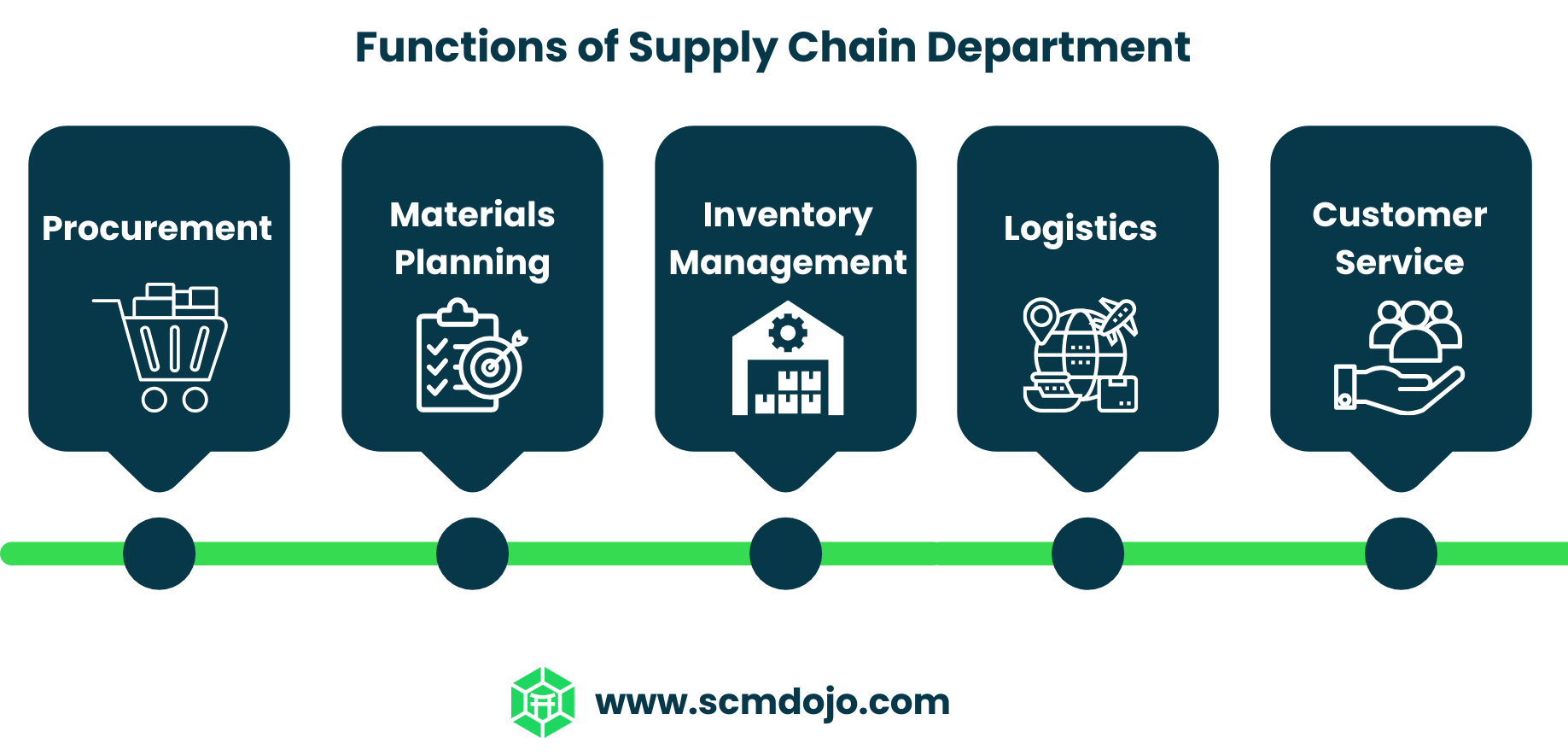
Functions of the Supply Chain Department
The supply chain department is responsible for a wide range of functions, each contributing to the overall efficiency of the supply chain. These functions include procurement, production planning, inventory management, logistics, and customer service.
Procurement
Procurement involves sourcing and acquiring the materials or products needed for production. Moreover, by selecting reliable suppliers, negotiating favorable terms, and ensuring timely delivery, the supply chain department can optimize procurement processes and minimize costs.
Materials Planning
Production planning is another critical function, as it involves scheduling production activities, allocating resources, and ensuring efficient utilization of equipment and labor. This includes implementing lean manufacturing principles and utilizing advanced planning software, so businesses can optimize production processes and minimize waste.
Demand Planning and Inventory management
Inventory management is crucial for ensuring adequate stock levels and minimizing carrying costs. By implementing inventory control techniques, such as just-in-time (JIT) or vendor-managed inventory (VMI), businesses can optimize inventory levels and improve cash flow. Demand planning predicts customer needs, inventory management keeps the right amount of stock on hand, and S&OP (Sales & Operations Planning) unites these functions. This dream team ensures production matches demand, reducing costs and stockouts while keeping customers happy.
Logistics
Logistics involves managing the transportation and delivery of goods. This includes selecting the most cost-effective carriers, optimizing routes, and utilizing technology solutions, so businesses can minimize lead times and improve customer satisfaction.
Customer service
Despite Customer service being an integral part of the supply chain, as it involves ensuring timely and accurate delivery, handling customer inquiries and complaints, and maintaining strong relationships with customers, they do not report to the Supply chain head. This includes providing excellent customer service, so businesses can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
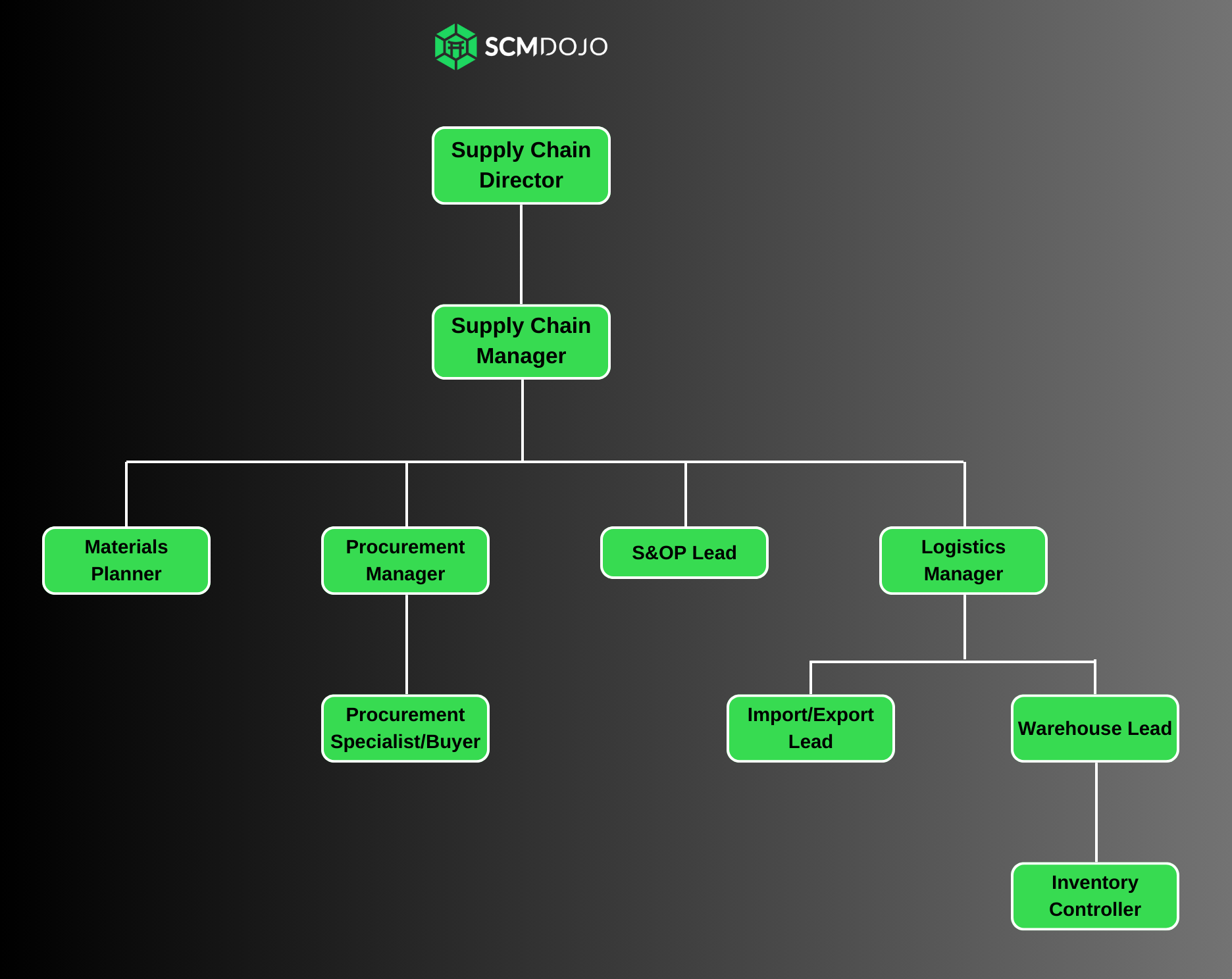
Key Roles of the Supply Chain Department Defined
Within the supply chain department, several key roles contribute to its efficient functioning. These roles include supply chain managers, procurement specialists, demand planners, logistics coordinators, and data analysts.
Supply chain management oversees all supply chain activities, ensuring that processes are streamlined, and performance goals are met. Furthermore, They are tasked with developing strategies, managing relationships with suppliers and partners, and continuously improving the supply chain.
Supply Chain Director
- Set strategic goals and objectives for the supply chain department.
- Provide leadership and direction to ensure the smooth operation of the supply chain.
- Analyze performance metrics and implement improvements to enhance efficiency.
Supply Chain Manager
- Oversee all supply chain activities to ensure efficiency and effectiveness.
- Develop and implement strategies to optimize the supply chain.
- Coordinate with various departments to meet production and delivery targets.
To run the department, a supply chain manager needs certain supply chain metrics and KPIs to improve performance. If you are responsible for supply chain KPIs, access our Supply Chain KPIs Dashboard!
Read more about Top 18 Supply Chain KPIs for the Supply Chain Team on our website SCMDOJO!
Materials Planner
- Forecasts material needs based on production plans and sales forecasts.
- Analyzes data to predict future inventory requirements and avoid stockouts.
- Creates and maintains bills of materials (BOMs) to specify components needed for each product.
- Communicate with suppliers to source materials, negotiate pricing, and ensure timely deliveries.
If you are responsible for planning the inventory of your organization, our Inventory Planning guide is a must-have for you! Grab yours now!
Procurement Manager
- Leads the sourcing strategy, finding qualified vendors and negotiating the best deals for materials and services.
- Oversees the procurement process, ensuring efficient ordering, timely deliveries, and adherence to company policies.
- Manages supplier relationships, fostering communication and building long-term partnerships.
- Analyzes procurement data to identify cost-saving opportunities and optimize spending.
Are you a procurement manager who needs to optimize their spending? Our Procurement KPIs Dashboard is perfect to help you manage and optimize your procurement processes. Access yours here!
Procurement Specialist/Buyer
- Source and acquire materials or products needed for production.
- Negotiate contracts and evaluate suppliers.
- Ensure timely delivery of goods and minimize procurement costs.
If you are responsible for the sourcing process, our course The Sourcing Process taught by our expert Maryna Trepova is all you need to learn from make or buy decisions to the key process for obtaining quotations. Enroll Now!
Demand planners / S&OP Lead
- Analyze historical data and market trends to forecast customer demand.
- Facilitate production planning and resource allocation.
- Optimize inventory levels to meet demand efficiently.
Being an S&OP lead is not an easy job. So if you want to run your Sales & Operations Planning Process smoothly, enroll in the course How to Run a S&OP Process – Benefits, Process Steps & Overcome Barriers taught by our expert Dr. Muddassir Ahmad.
Logistics Manager
- Planning and coordinating transportation, distribution, and warehousing activities to ensure efficient product flow.
- Optimizing logistics processes to minimize costs and reduce lead times.
- Managing relationships with carriers, suppliers, and logistics service providers to meet customer requirements.
Are you responsible for measuring key performance indicators for the supply chain in your organization? Get the Logistics KPI Dashboard Excel Template – your essential companion for Logistics & Supply Chain Management.
Logistics Coordinators
- Manage transportation and delivery of goods.
- Coordinate with carriers and optimize routes.
- Ensure timely and cost-effective delivery
Warehouse Lead
- Oversee warehouse operations and staff.
- Ensure efficient receipt, storage, and dispatch of goods.
- Maintain a safe and organized warehouse
If you are confused about determining whether your warehouse is operating at a satisfactory level, grab this warehouse audit tool or Warehouse Audit Checklist, which empowers you to pinpoint areas that require enhancement and gauge the performance of your warehouse.
Import / Export Lead
- Overseeing import/export operations, including documentation, customs compliance, and shipping arrangements.
- Developing and implementing import/export strategies to expand market reach and increase sales.
- Ensuring compliance with international trade regulations and managing relationships with overseas partners.
If you are involved in global trade, you need to enroll in our Global Trade Compliance course. It is dedicated to helping those within the supply chain industry to learn how organizations manage their fulfillment of government regulations while doing global trade.
Inventory Controller
- Manage inventory levels and stock movement.
- Conduct regular audits and reconcile inventory discrepancies.
- Implement inventory control measures to minimize losses and optimize stock levels.
Are you worried about the discrepancies in your stock? The objective of this Cycle Counting Procedure is to establish guidelines and requirements for the implementation of Cycle Counting Programs across all business processes and sites to address these discrepancies in quantities. Get your guide now!
Measuring and Monitoring Supply Chain Performance
To ensure continuous improvement in the supply chain department, businesses need to measure and monitor performance regularly. By defining key performance indicators (KPIs) and utilizing performance management tools, businesses can track progress and identify areas for improvement.
Some common KPIs for supply chain performance include on-time delivery, order fulfillment cycle time, inventory turnover, and customer satisfaction. By regularly monitoring these metrics, businesses can identify trends, benchmark performance against industry standards, and take proactive measures to improve performance.
Additionally, businesses can utilize performance management tools, such as dashboards or scorecards, to visualize and analyze performance data. These tools provide real-time insights into key metrics, allowing for better decision-making and continuous improvement.
Conclusion: Streamlining Your Supply Chain for Success
In essence, in today’s competitive landscape, an efficient supply chain is no longer a luxury, it’s a necessity. By implementing a structured approach and fostering collaboration across departments, businesses can unlock the true potential of their supply chain. This translates to significant benefits of reduced costs, enhanced customer satisfaction, increased efficiency, and improved risk management. Moreover, a well-structured supply chain department, staffed with skilled professionals, forms the backbone of this success. This includes focusing on key functions like procurement, planning, logistics, and performance measurement, so businesses can achieve optimal efficiency and drive long-term growth.
Lastly, this investment in a streamlined supply chain empowers businesses to deliver the right products, to the right customers, at the right time – every time.