Ever wonder how Amazon gets your package to your door so quickly? The inner workings of logistics at Amazon are a marvel of efficiency, precision, and constant innovation. This system uses giant warehouses, lots of trucks, and even cool robots to move things quickly. In this blog post, we’ll explore how Amazon does it all.
We’ll look at their warehouses, their delivery tricks, and even how they use new technology to make things faster. Peek behind the curtain of Amazon’s speedy deliveries! We’ll explore their logistics empire, from warehouse robots to futuristic visions, and discover how they manage millions of packages daily. Get ready to dive into the $574 billion machine and see what Amazon has planned for the future of delivery!
Amazon’s Mission
Its unwavering commitment to customer satisfaction is at the heart of Amazon’s logistics strategy. From the very beginning, Amazon’s mission has been to be the earth’s most customer-centric company. This customer-focused approach permeates every aspect of their operations, including logistics.
By prioritizing the needs and desires of their customers, Amazon has built a loyal following who have come to expect fast and reliable delivery. This has allowed them to leverage their logistics capabilities as a competitive advantage, setting them apart from their competitors.
Services by Amazon
Here are some of the key services offered by Amazon:
- General public: Amazon.com – an e-commerce platform offering a diverse selection of products such as books, electronics, apparel, and groceries.
- Marketplace: Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) – Enables third-party sellers to utilize Amazon’s logistics and delivery infrastructure.
- Content creation: Amazon Studios – Produces original films and series available for streaming on Amazon Prime Video.
- Cloud and Machine Learning services: Amazon Web Services (AWS) – Provides cloud computing infrastructure, storage solutions, and machine learning services to businesses and developers worldwide.
- Prime Membership: Amazon Prime – Subscription service offering benefits such as free two-day shipping, access to Prime Video, Prime Music, and exclusive deals.
- Digital Content: Amazon Prime Video and Amazon Music – Streaming services offering a vast library of movies, TV shows, music, and original content.
- Grocery Delivery: Amazon Fresh – Allows customers to order groceries online for delivery or pickup.
- Smart Home: Amazon Alexa – Virtual assistant technology integrated into Amazon Echo devices for voice-controlled smart home automation and information retrieval.
- Advertising: Amazon Advertising – Suite of advertising solutions for sellers and brands to promote their products on Amazon’s platforms.
- Handmade Crafts: Amazon Handmade – Marketplace for artisans to sell their handmade goods directly to customers.
- Pharmacy: Amazon Pharmacy – Online service for purchasing prescription medications with home delivery.
- Business Solutions: Amazon Business – Marketplace offering tailored products and tools for businesses, including bulk purchasing and business pricing.
- Convenience Stores: Amazon Go – Physical stores with cashier-less checkout technology for quick and convenient shopping experiences.
- Try Before You Buy: Amazon Prime Wardrobe – Service allowing Prime members to try on clothing and accessories before purchasing them.
- Logistics: Amazon Logistics – Amazon’s in-house delivery network is responsible for customer package delivery.
Amazon Clients & Services
Amazon’s logistics prowess extends beyond its operations. The company also offers a range of logistics services to third-party sellers, allowing them to tap into Amazon’s extensive network and benefit from the same efficient delivery options.
Through Amazon’s Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) program, sellers can store their products in Amazon’s fulfillment centers, where Amazon takes care of the picking, packing, and shipping. This enables sellers to reach a broader customer base and offer fast delivery options, even if they do not have the infrastructure to do so themselves.
Additionally, Amazon’s logistics services include transportation and warehousing solutions, allowing businesses of all sizes to leverage Amazon’s expertise and resources in streamlining their supply chain and improving their delivery capabilities.
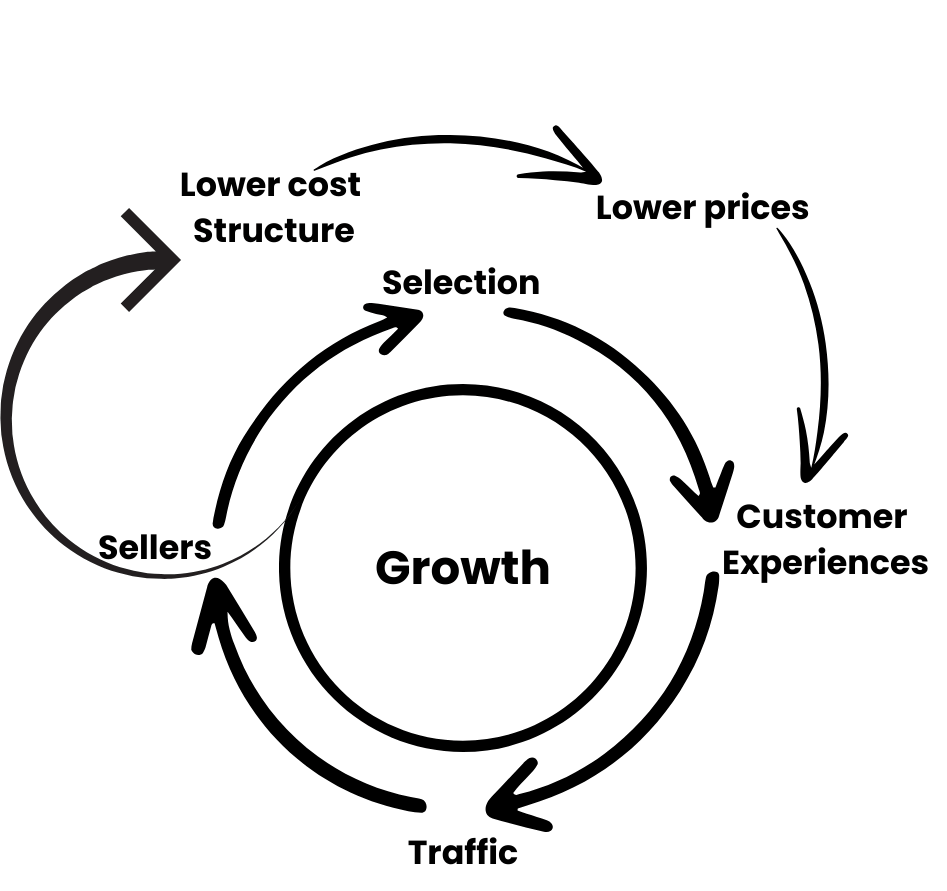
Amazon’s Virtuous Circle
One of the key elements of Amazon’s logistics strategy is what they refer to as the “virtuous circle.” This concept revolves around the idea that increased selection leads to more customers, which in turn drives more sellers to join the platform, resulting in lower prices and even greater selection.
By continuously expanding their product range and attracting more sellers, Amazon can offer customers a vast selection of items to choose from. This abundance of options not only increases customer satisfaction but also allows Amazon to optimize its logistics operations.
With a wide array of products stored in its fulfillment centers, Amazon can consolidate orders and optimize its inventory management systems. This reduces the need for multiple shipments and allows for more efficient use of their warehouse space, ultimately leading to faster and more cost-effective deliveries.
Amazon Product Range
One of the key drivers of Amazon’s success in logistics is the sheer breadth of its product range. From books and electronics to clothing and groceries, Amazon offers an unparalleled selection of items to its customers.
This extensive product range presents unique challenges for logistics, as each item has different storage and handling requirements. To overcome this, Amazon has developed sophisticated inventory management systems that allow them to efficiently store and retrieve products from their fulfillment centers.
By categorizing products based on size, weight, and other attributes, Amazon can optimize its warehouse layout and minimize the time and effort required to locate and pick items for delivery. This level of precision and automation in their inventory management is crucial in achieving the fast and reliable deliveries that Amazon is known for.
Access all the courses related to logistics on our website SCMDOJO
Amazon Figures
Here’s a breakdown of the latest Amazon figures you requested (as of April 2, 2024):*
- Turnover in 2023: $574 billion
- Profit in 2023: $30.4 billion (net profit)
- Profit by Region/Country: North America is a major market, followed by Europe and Asia.
- Sales by Region/Country: North America is likely the biggest contributor (395.64 Billion US Dollars), followed by Europe and potentially Asia.
- Total Number of Employees: Amazon doesn’t disclose their total employee count for the latest year (2023). 2021: 1,608,000 Amazon Employees
- New hires: However, in 2022, they employed over 1.5 million people globally
Where Amazon spends the most:
This can vary depending on the quarter or year, but major spending areas include:
- Fulfillment Network: Warehouses, transportation, and delivery infrastructure.
- Technology and Development: Building and maintaining the Amazon Web Services (AWS) infrastructure and other technological advancements.
- Marketing and Advertising: Attracting new customers and promoting products and services.
- Content Acquisition: For Amazon Prime Video, Twitch, and Audible.
- High Seasonality: Amazon experiences a significant sales surge during the holiday season, typically from November to December, due to Black Friday, Cyber Monday, and holiday shopping.
Factors Affecting Profit:
Several factors can impact Amazon’s profit, including:
- Overall economic conditions: A strong economy generally leads to increased consumer spending, benefiting Amazon.
- Competition: Price competition from other retailers can affect profit margins.
- Fulfillment Costs: The efficiency and cost of managing their vast fulfillment network can significantly impact profit.
- Investment in Growth: Amazon frequently invests in new technologies, services, and acquisitions, which can impact short-term profits but benefit long-term growth.
Amazon Prime and Its Impact on Delivery Speed
One of the most significant developments in Amazon’s logistics strategy was the introduction of Amazon Prime. This subscription-based service offers customers free two-day shipping on eligible items, revolutionizing the e-commerce industry and setting new delivery standards.
Amazon Prime has had a profound impact on delivery speed and customer expectations. By incentivizing customers to become Prime members, Amazon has created a loyal customer base that prioritizes fast delivery and is willing to pay a premium for it.
To meet the demands of Prime members, Amazon has invested heavily in expanding its fulfillment center network and optimizing its logistics operations. This includes the use of advanced technologies such as robotics and AI to increase efficiency and reduce delivery times.
Amazon Logistics
Fulfillment Centers:
- Estimated number: Over 185 globally (as of 2024, exact numbers can fluctuate)
- Function: These are massive warehouses where Amazon stores a wide variety of products. They’re equipped with advanced technology like robots and sophisticated inventory management systems to efficiently pick, pack, and ship your orders.
- Size: Can range from 80,000 square meters (around 860,000 square feet) to much larger.
Delivery Stations:
- Estimated number: Over 1,500 globally (as of 2024, this is an estimate based on industry reports)
- Function: These are smaller facilities strategically located closer to urban areas. They receive packages from fulfillment centers and sort them for final delivery by Amazon drivers or independent delivery partners. This allows for faster last-mile delivery to customers.
- Size: Smaller than fulfillment centers, often located in industrial areas.
Sortation Centers:
- Estimated number: Around 80 globally (as of 2024, numbers may vary)
- Function: These facilities act as distribution hubs, typically located near fulfillment centers. Packages are received from fulfillment centers, sorted based on destination, and then sent to delivery stations or directly to regional hubs for further distribution.
- Size: Can vary depending on location and volume handled.
Pantry & Fresh Food Distribution Centers (DCs):
- Estimated number: While Amazon doesn’t disclose the exact number, they have a growing network of Pantry and Fresh Food DCs globally. Estimates suggest several hundred facilities dedicated to these categories (figures aren’t publicly available).
- Function: These DCs differ from standard fulfillment centers in terms of temperature control. Pantry items typically require ambient storage, while Fresh items need refrigeration or freezing depending on the product. These DCs cater specifically to perishable goods and ensure they maintain proper temperatures throughout storage and fulfillment.
- Size: Sizes likely vary depending on location and demand, but they’re generally smaller than standard fulfillment centers due to the specialized storage requirements.
Whole Foods Retail Integration:
- Estimated number: Over 570 physical Whole Foods Market stores globally (as of April 2024).
- Function: Whole Foods serves a dual purpose within Amazon’s logistics network.
- Delivery & Pickup: Customers can order groceries online from Whole Foods for delivery or pickup at a nearby store. This leverages existing store infrastructure for last-mile delivery of fresh groceries.
- Fulfillment Network Integration: Some Whole Foods locations may also function as mini-fulfillment centers for specific areas. They can store and fulfill online orders for both Whole Foods products and Pantry items.
Airport Hubs:
- Number: One airport hub is under construction in Kentucky.
- Function: Airport hubs serve as crucial points for moving large quantities of goods quickly across long distances. Perishable goods like fresh food may utilize air freight for faster delivery to distant locations. Amazon likely relies on a combination of its own facilities and partnerships with existing cargo hubs at airports.
Amazon’s Innovation in Logistics
Faster Deliveries with “Anticipatory Package Shipping” (Filed August 2012)
Imagine Amazon predicting what you’ll buy before you do! This patent outlines a system where popular items are shipped to a general area near potential customers, even before a specific order is placed. By analyzing customer data and buying habits, Amazon aims to significantly reduce delivery times.
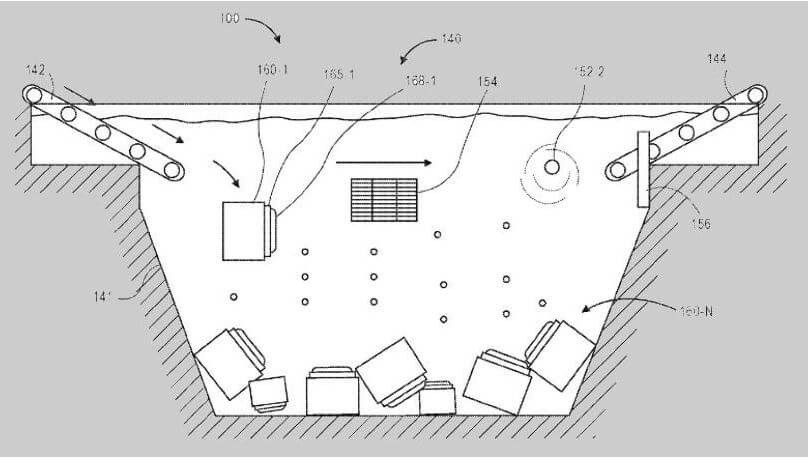
Thinking Outside the Box: Underwater Warehouses (Filed September 2016)
This “out there” patent might be a genius! It proposes storing products in giant underwater storage facilities. Items would be equipped with special devices to control their depth, allowing them to rise to the surface when needed for shipping. This could free up space in traditional warehouses and be ideal for storing bulky items or those with fluctuating demand.
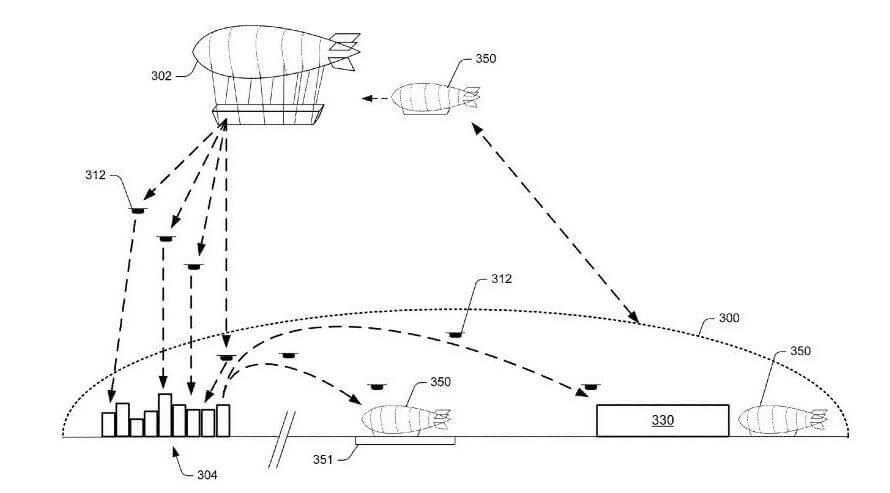
Flying High with Airborne Fulfillment Centers (Filed December 2016)
Amazon’s drone delivery dreams get a boost with this patent. It describes massive floating warehouses positioned high in the sky. Drones stationed there could then deliver packages using minimal energy for descent. This “mobile warehouse” concept allows drones to cover a wider area and be closer to where deliveries are needed.
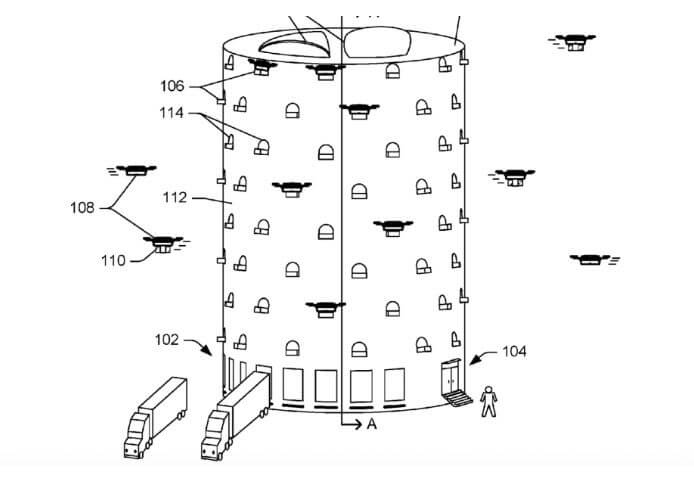
Urban Beehives: Multi-Level Drone Warehouses (Filed December 2015)
This patent envisions a future where drones take center stage in deliveries. Imagine giant, multi-level warehouses resembling beehives located in cities. These would act as hubs for drones, allowing them to pick up packages and return for re-loading by robots or humans. Super fast and on-demand deliveries through the air? That’s the vision here.
Steering the Future: Lane Assignments for Autonomous Vehicles (Filed January 2017)
This patent focuses on autonomous vehicles, a technology Amazon is clearly interested in. It outlines a system where self-driving cars can navigate special lanes that change direction based on traffic needs. Amazon’s design allows communication between cars and this system, potentially leading to smoother traffic flow and faster deliveries.
Beyond Delivery: On-demand Apparel Manufacturing (Filed December 2015)
This patent hints at Amazon’s ambitions beyond just logistics. It describes a system for on-demand apparel manufacturing, allowing for custom-made clothes delivered quickly. This aligns with Amazon’s recent forays into the clothing industry, suggesting they might disrupt the traditional apparel retail model.
Key Takeaways:
- These patents showcase how Amazon is constantly innovating and thinking ahead. They’re not just focused on improving current systems but exploring futuristic possibilities.
- Controlling their delivery infrastructure seems to be a priority for Amazon, with patents on drones, autonomous vehicles, and underwater storage.
- While some ideas might seem far-fetched, they offer a glimpse into how Amazon envisions the future of logistics and retail.
Technology and Automation in Amazon’s Logistics Operations
1. Smart Warehouse Software: The Brain of the Operation
Imagine a super-organized brain keeping track of everything in a giant warehouse. That’s what Amazon’s Warehouse Management System (WMS) does. This software knows where everything is stored and how to get it to the packing stations quickly. It helps avoid mistakes and keeps things running smoothly.
2. Robots: Your Speedy Warehouse Helpers
Ever seen a robot in a movie zipping around and picking things up? Well, Amazon uses similar robots in their warehouses! These robots help pick and pack your orders, making the process much faster than if everything were done by hand.
3. Data Drives Efficiency: Making Smart Delivery Decisions
Amazon is a data whiz! They use information about what people order, when they order it, and where they live to figure out the best ways to deliver packages. This data helps them optimize delivery routes and make sure your order gets to you as quickly as possible.
Amazon’s Warehouse Automation
One of the key elements of Amazon’s logistics strategy is its extensive use of warehouse automation. By implementing cutting-edge technology and robotics, Amazon has revolutionized the way products are picked, packed, and shipped within their fulfillment centers.
Robotic fulfillment systems, such as Amazon’s Kiva robots, have greatly increased efficiency and speed in their warehouses. These robots work alongside human employees, bringing entire shelves of products to them, reducing the time spent searching for items. With the help of these robots, Amazon can fulfill customer orders at a rate that was previously unimaginable.
In addition to robotics, Amazon also utilizes advanced inventory management systems that optimize the placement of products within their warehouses. By analyzing data on product demand and popularity, Amazon strategically positions items closer to the packing stations, reducing the time and effort required to fulfill orders. This meticulous inventory management ensures that popular items are readily available for quick delivery, while less popular items are stored in more space-efficient locations.
Amazon’s warehouse automation not only speeds up the fulfillment process but also minimizes errors and improves overall accuracy. With the help of advanced algorithms and real-time data, Amazon can ensure that the right products are picked and packed for each customer order, reducing the likelihood of mistakes and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Last-mile delivery and Amazon’s innovative solutions
Last-mile delivery, or the final leg of the delivery process from the distribution center to the customer’s doorstep, is often the most challenging and costly part of logistics. Recognizing this, Amazon has implemented several innovative solutions to overcome the last-mile delivery bottleneck.
Amazon Locker:
One such solution is Amazon Locker, a self-service delivery option that allows customers to pick up their packages from secure, self-service lockers located in public places such as grocery stores and convenience stores. This eliminates the need for multiple delivery attempts and ensures that customers can receive their packages at their convenience.
Drones:
Amazon has also experimented with alternative delivery methods, such as drones and autonomous vehicles. Through its Prime Air program, Amazon aims to use drones to deliver packages within 30 minutes of ordering.
Autonomous Vehicles:
Similarly, their investment in autonomous vehicle technology could revolutionize the last-mile delivery process, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
Amazon Transport and Prime Air
Another crucial aspect of Amazon’s logistics strategy is its transportation network. By establishing their delivery infrastructure, Amazon can have greater control over the entire delivery process, from the moment an order is placed to its final destination.
Amazon has a fleet of delivery vehicles, including vans and trucks, that enables them to handle a large volume of deliveries efficiently. By leveraging advanced routing algorithms and real-time traffic data, Amazocanto optimizes delivery routes and minimizes delivery times. This level of control allows them to offer expedited delivery options, such as same-day or next-day delivery, which have become synonymous with Amazon’s brand.
In recent years, Amazon has also ventured into the world of aerial delivery with its Prime Air service. Using drones, Amazon aims to revolutionize the last-mile delivery process by delivering packages directly to customers’ doorsteps. While the service is still in its early stages, Prime Air has the potential to further enhance Amazon’s delivery speed and efficiency, especially in densely populated urban areas.
By investing in its transportation network and exploring innovative delivery methods like Prime Air, Amazon has been able to reduce reliance on third-party logistics providers and gain greater control over the entire delivery process. This level of control has been instrumental in their ability to consistently deliver packages quickly and reliably.
Lessons that Other Businesses Can Learn from Amazon’s Logistics Success
Amazon’s logistics success can serve as a valuable lesson for businesses of all sizes and industries. Here are some key takeaways that can be applied to improve delivery efficiency:
Invest in technology and automation: By embracing cutting-edge technology and automation, businesses can streamline their fulfillment processes, increase efficiency, and reduce errors. From warehouse robotics to inventory management systems, technology can be a game-changer in achieving efficient delivery.
- Optimize inventory management: Analyzing data on product demand and popularity can help businesses strategically position items within their warehouses, minimizing the time and effort required to fulfill orders. By ensuring popular items are readily available and less popular items are stored in more space-efficient locations, businesses can improve overall efficiency.
- Establish a reliable transportation network: Having control over the delivery process can significantly improve efficiency. By investing in the delivery infrastructure, businesses can optimize delivery routes, reduce delivery times, and offer expedited delivery options.
- Prioritize customer satisfaction: At the end of the day, customer satisfaction should be the driving force behind any logistics strategy. By obsessing over meeting delivery promises and constantly seeking ways to improve the customer experience, businesses can build a loyal customer base and differentiate themselves from the competition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Amazon’s logistics strategy is a masterclass in efficient delivery. Through warehouse automation, advanced inventory management, and its transportation network, Amazon has set the standard for fast and reliable e-commerce fulfillment. By prioritizing customer satisfaction and continuously investing in technology and innovation, Amazon has cemented its position as the undisputed leader in the world of e-commerce logistics.
Other businesses can learn valuable lessons from Amazon’s success and apply them to improve their delivery operations. As the e-commerce landscape continues to evolve, the importance of efficient logistics will only grow, making Amazon’s logistics strategy a blueprint for success in the digital age.
References
https://www.junglescout.com/blog/amazon-statistics/.
https://www.businessofapps.com/data/amazon-statistics/
https://www.doofinder.com/en/statistics/how-many-employees-does-amazon-have
https://www.techgistics.net/blog/2017/9/28/connecting-the-dots-on-amazons-patents-in-logistics
https://www.statista.com/statistics/672782/net-sales-of-amazon-leading-markets/