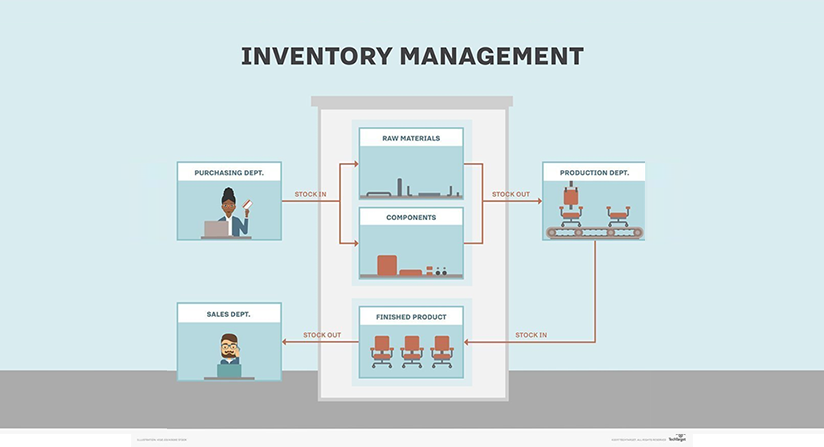
Digital transformation is aggressively scaling up across all sectors of the manufacturing industry. Technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, Robotics, 3D printing, Virtual Reality, and Augmented Reality are transforming the manufacturing world. In this blog, we will learn about Extended Reality (XR), which is a superset of emerging technologies, such as Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, and Mixed Reality.
To understand the term Extended Reality, it is essential to learn about technologies that are part of Extended Reality (XR) – Augmented, Virtual and Mixed Reality.
What is Augmented Reality (AR)?
Augmented Reality has been increasingly adopted in the manufacturing industry due to its potential to revolutionize manufacturing operations such as designing, prototyping, maintenance, and assembly.
- Augmented Reality uses computer-generated perpetual information and virtual objects and puts them in the real world. It helps humans access the real world while interacting in 3D dimensions.
- Augmented Reality superimposes digital information onto natural objects to promote human interaction between the physical and digital worlds. An AR-enabled device with an in-built camera helps workers identify objects and pieces of machinery in the middle of a warehouse or shop floor.
- An AR-enabled device is designed to download information about the object from the cloud platform. With trackers such as GPS, barometric sensors, and accelerometers, smart devices can superimpose digital information over an area or object. It creates a 3D interface.
- Real-time data and the use of smart devices help users interact with the object and send commands by voice, message, or gestures. So, managers can monitor the operations and handle the workforce without being present on the shop floor.

What is Virtual Reality?
Virtual Reality is another term that helps users explore and interact with virtual surroundings in a way that approximates reality. Users might need external gear, such as helmets or goggles, to witness the virtual environment. Virtual Reality creates a computer-generated world that fully immerses users in the virtual surroundings. Everything you see is part of the environment artificially created through images or sound.
Virtual Reality can benefit the manufacturing industry by simulating a manufacturing process while allowing manufacturers to identify equipment placement, workflow, or more challenges.
VR helps predict hazards and risks associated with the use of assembly lines. Virtual scenarios can help manufacturers in activities such as guiding a new person with complex processes, providing remote assistance to users in another country, and more. With Virtual Reality training development, you can provide real-time guidance and instruction while helping organizations relocate resources. Highly educated or trained employees can work on critical business matters, ultimately boosting the business’s bottom line.
What is Mixed Reality?
Mixed Reality combines AR and VR, allowing humans to interact with the digital world and the real world simultaneously. Backed by holographic technology, Mixed Reality devices are more powerful and more expensive than VR devices. It allows you to view your entire surroundings and interact in that environment. Meanwhile, in the MR headset, humans can be active and perform activities. Let’s see how Mixed Reality helps manufacturers with streamlining their operations:
- Virtual prototyping: MR enables professionals to create and test virtual prototypes before initiating physical production. For example, automobile manufacturers can visualize and manipulate 3D models of the vehicles, saving time and money while producing the automobiles.
- Training and simulation: MR technology allows manufacturers to provide better employee training in a safe and controlled environment. Manufacturers can use MR in assembly training so employees can reach productivity levels quickly.
- Quality assurance and inspection: Employees can compare physical models with digital products in real-time to identify potential errors, and enable quicker resolution.
- Assembly line optimization: MR-based systems provide workers with visual assistance, cues, and guidance. It helps streamline assembly line workflows.
Mixed Reality is the future of the manufacturing sector. From guiding technicians through maintenance tasks to allowing operators to visualize and optimize the factory floor through digital twins, MR technology can facilitate ease and better decision-making in the manufacturing sector.

Extended Reality (XR) combines three powerful technologies: Augmented, Virtual, and Mixed Reality. The advantages of XR in manufacturing extend beyond streamlining functions, predicting costs, and reducing errors and waste. XR enhances safety and training sessions, floor planning, new product development, and product assembly, increasing customer engagement and more.
How do Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality affect ERP software?
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality will change ERP systems in the following ways.
Better training systems
With an ERP system, you will require human instructors who will need to make the sessions interactive. On the other hand, with AR-enabled devices, you can connect employees with remote instructors in real time, eliminating the need for trainers to travel from one place to another. Also, VR-enabled devices will promote robot instructors who are trained to connect with humans and assist them in the best possible manner.
Improved order picking
Order picking is the first step in fulfilling customers’ orders, and it is essential to process the remaining processes, which include order packing, shipping, and post-delivery service. Order picking is a time-consuming process for the logistics department, requiring scanning multiple barcodes to locate items. With Augmented Reality technology, employees can use smart scanning devices to help them find and collect the right items to ensure timely delivery.
Ergonomic analysis
High-tech gadgets and MR-enabled devices can help operators discover and address ergonomic issues in the manufacturing environment. It allows employees to analyze workstation ergonomics and reduce the risk of injury.
Marketing and sales
Gone are the days when marketing executives used to roam around cities to present their products. With MR-enabled gadgets, customers can explore products in the virtual environment. Porsche, A German automobile company, Porsche uses mixed reality to show vehicle customization options. This offers an immersive customer experience.
Conclusion
The integration of Extended Reality into manufacturing operations has significantly improved efficiency and business productivity and will continue to do so. As this technology advances, we can expect more significant advancements in the manufacturing sector, leading to a more sustainable future. From monitoring and optimizing manufacturing consumption in the organization to enhancing supply chain management, Extended Reality, a combination of Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, and Mixed Reality, revolutionizes the manufacturing landscape.
Follow Us