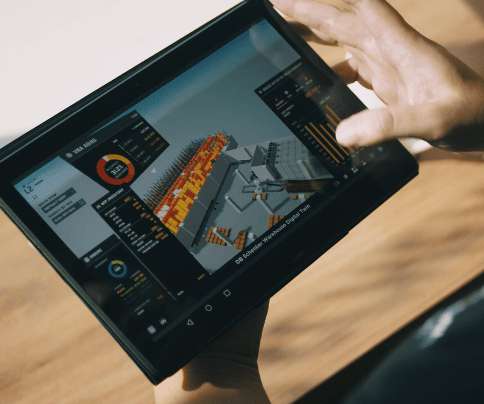
DB Schenker – Singapore: A Vital Node in Singapore’s Logistics Ecosystem
The Logistics & Supply Chain Management Society
NOVEMBER 15, 2021
Singapore’s Status a Global Hub. From its peak, 97% flight capacity was reduced from Singapore Airlines. Typically, 45% to 50% of cargo is carried in belly holds of aircraft. With such dramatic reductions in flights, Singapore’s status of a logistics hub was put severely at risk. Keeping Supply Chains Moving.









Let's personalize your content