What role can technology play in transforming the food and drink industry for the better?: transparency roundup
Provenance
APRIL 10, 2019
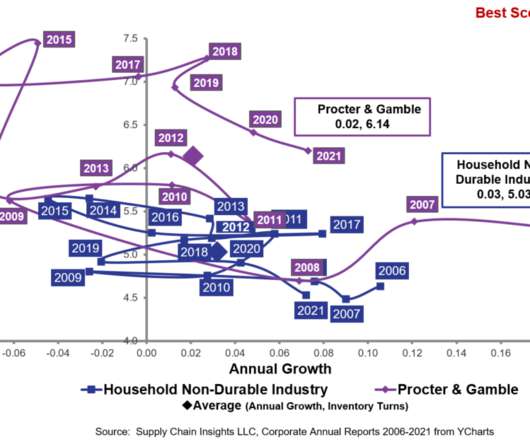
“For every $1 spent on food, society pays $2 in health, environmental, and economic costs” (Source: Ellen MacArthur Foundation ). The comprehensive report, “Cities and Circular Economy for Food” from the Ellen Macarthur Foundation, looks to address key challenges created by the food industry today: Annual costs of $5.7










Let's personalize your content