What Caused the Baby Formula Shortage + 7 Ways Consumers and Companies are Coping
ToolsGroup
MAY 18, 2022
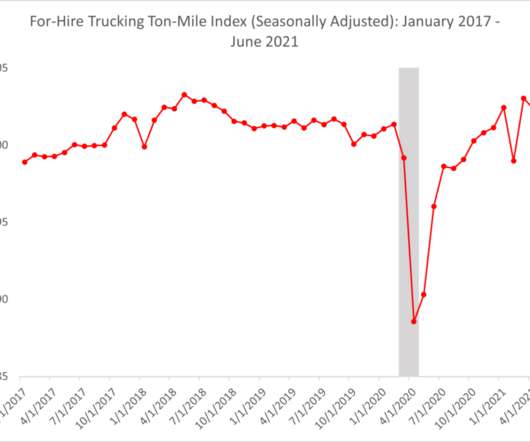
Data also shows that half of US states are experiencing out-of-stock rates between 40% and 50%: Image source: Flipboard. This made it incredibly difficult for manufacturers to accurately gauge the market size for production. Image source: Sturgis Journal. A Limited Number of Formula Manufacturers. Image source: MTL Blog.







































Let's personalize your content